The two-sided ladder formation of the double-helix DNA structure. What bond provides the three dimensional structure of large.
The nucleoside triphosphates are the common monomers.

. This is also known as the beads on a string structure. DNA is essentially made of sugar phosphate and bases bonded together by hydrogen. Some of these include.
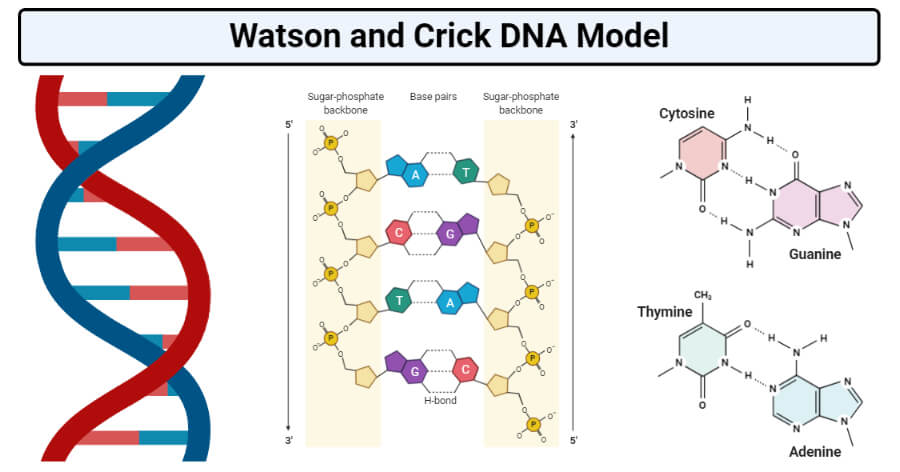
The three-dimensional structure of DNA the double helix arises from the chemical and structural features of its two polynucleotide chains. DNA contains the nucleotide bases adenine thymine. The helix of D-DNA is twisted in a right-handed fashion and called the poly dA-dT and poly dG-dC form.
Identify the key structural features of a DNA molecule DNA strands are antiparallel and include a 5end and a 3end. DNA molecules arrange themselves in a model called the DNA double helix. The size and shape of the C-DNA are smaller than the B-DNA and A-DNA.
Biology 1 Answer Vincent G. The bases A G C G form the rungs of the ladder. Chromosomal DNA consists of two DNA polymers that make up a 3-dimensional 3D structure called a double helix.
So Dina is a double helix uh strained. This fiber is further coiled into a thicker and more compact structure. Both the strands.
Several scientists were chasing after the DNA structure structure meaning understanding how the DNA chain adopts a three-dimensional shape. 1 the progress made by X-ray crystallographers in studying organic macromolecules. 3 DNA structure DNA is the molecule that holds the instructions for growth and development in every living thing.
The three-dimensional structure of DNAthe double helixarises from the chemical and structural features of its two polynucleotide chains. A double helix discovered by Watson and Crick who were leaked data from Rosalin Franklin. Because these two chains are held together by hydrogen bonding between the bases on the different strands all the bases are on the inside of the double helix and the sugar -phosphate backbones are on the outside see Figure 4-3.
Jul 16 2016 Picture a ladder twisted from top to bottom. This is much like what a strand of DNA looks like. Strong ionic bonds and hydrophobic interaction hold DNA together.
In a double helix structure the strands of DNA run antiparallel meaning the 5 end of one DNA strand is parallel. Picture a ladder twisted from top to bottom. Briefly describe the three-dimensional structure of DNA.
Discuss other three-dimensional structures that DNA may adopt and how these structures may affect its biological function Introduction DNA known as deoxyribosenucleic acid is the primary genetic unit of most organisms on Earth. Remember that the phosphate and sugar molecules are the backbones of the ladder. Describe the 3 dimensional structure of DNA.
A well-known form of DNA that can be found in a vast majority of living cellular organelles is the three-dimensional B form of DNA introduced by Watson and Crick1953 a right-handed double-helix with the two strands running antiparallel. In the cell D-DNA is found very rarely. Step 1 of 4.
- Answers The DNA molecule is shaped like an extremely long ladder twisted into a helix similar in appearance to the shape of a spiral. Watson Crick and Wilkins described the structure of DNA but also indicated how it could be replicated and transfer from one organism to its off spring. D-form consists of 8 base pairs per turn which are displaced backwardly with respect to the DNA-helix.
Therefore all the bases are on the inside of the double helix and the sugar-phosphate backbones are on the outside. Its a 3-D structure that is stored in the nucleus of all cells. Describe the key feature of the three-dimensional structure of the B-form of DNA.
What is the name used to describe the 3-dimensional structure of DNA. The nearly planar and hydrophobic bases are stacked inside the helix relatively perpendicular to the backbone. Cellular DNA molecules have two polynucleotides that spiral around an imaginary axis this forms a double helix.
Salient features of double helix structure of DNA include. So describe the three dimensional structure of DNA. While the discovery of the structure of DNA involved four scientists many scientific breakthroughs had to occur for the structure of DNA to be found.
But were did a and then were gonna have another one. Its structure is described as a double-stranded helix held together by. The two DNA strands are held together by hydrogen bonding between the bases on the different strands.
Which of the following does not describe an aspect of the three- dimensional structure of the DNA helix. 2 the growing evidence supplied by geneticists that it was DNA not protein in. So first of all theyre anti parallel meaning one will be going from this reform to five prime.
An oligopeptide has the ff amino acid composition. What is the three-dimensional shape of the DNA molecule. This is much like what a strand of DNA looks like.
Watson and Crick two young scientists at the Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge England wanted to make a model effectively a guess or hypothesis of what DNA might look like based upon a minimal. 2 Phe 2 Met 2 Glu 1 Arg 1 Val 1 Leu. The nitrogenous bases in DNA for hydrogen bonds in a complementary fashion A T C G.
The structure is called a double helix. The nucleosomes are the beads and the short lengths of DNA between them are the string The nucleosomes with their DNA coiled around them stack compactly onto each other to form a 30-nmwide fiber. If this was our day it would only be a single helix.
Double helix made of two polynucleotide chains. The double helix consists of two antiparallel nucleotide strands. Sugar and phosphate form backbone and N-base project inside.
Replication of DNA mean formation of an. In DNA the 5 carbon-sugar is deoxyribose. In order to understand the three-dimensional structure of DNA its convenient to think of DNA as a ladder-like molecule with a very regular structure as shown below.
It is clear that DNA is responsible in composing larger. A nucleotide is a nucleoside joined with the one or more phosphoryl groups by an ester linkage ribose sugar base phosphate. These are the enzymes which catalyze the replication of DNA.
What a Strand of DNA Looks Like. The hydrogen bonding between base pairs is responsible for forming the. In DNA the four nucleosides that occur are deoxyadenosine deoxyguanosine deoxycytidine and deoxythymidine.
So were gonna have when he looks. The structure is called a.

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks

How To Make A 3d Dna Model Project Biology Wise

Resource Center Aging Part 2 Cell Biology Notes Biology Lessons Biology Notes
0 Comments